Explain Different Types of Constraints in Dbms
For binary relationship set R on an entity set A and B there are four possible mapping cardinalities. Type of domain constraints.

Structural Constraints Of Relationships In Er Model Geeksforgeeks
The UNIQUE constraint uniquely identifies each record in a database table.
. UNIQUE Constraint enforces a column or set of columns to have unique values. The types of cardinality constraints are mentioned below. In this article we will learn about Participation constraints in DBMS.
The DEFAULT constraint provides a. We have 5 types of key constraints in DBMS NOT NULL. Constraints can be column level or table.
The data type of a domain can be string integer. Unique keys are defined at table. Constraint Types DEFAULT.
SQL Constraints are rules used to limit the type of data that can go into a table to maintain the accuracy and integrity of the data inside table. Referential Integrity constraints in DBMS are based on the concept of Foreign Keys. A PRIMARY KEY constraint automatically has a.
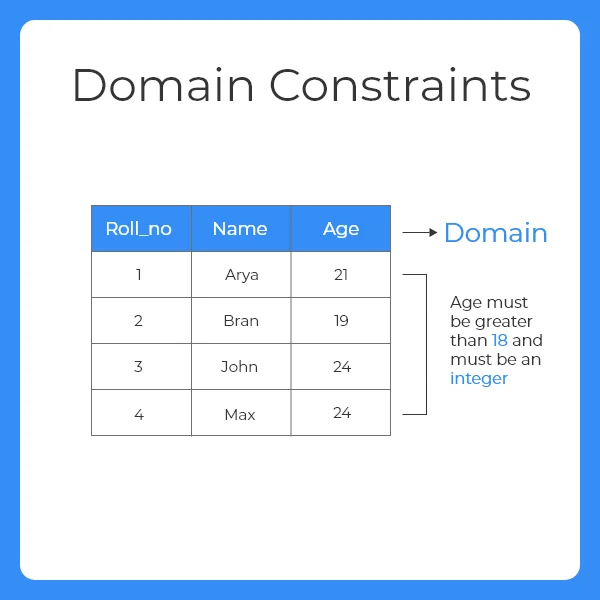
Domain Constraints Not Null. It is also called the minimum cardinality constraint. There can be more than one key in the table but it can have only one primary key.
A NOT NULL constraint is a rule that prevents null values from being entered into one or more columns within a table. Ensures that the specified column doesnt contain a NULL value. Domain integrity means the definition of a valid set of values for an attribute.
Domain integrity constraint contains a certain set of rules or conditions to restrict the kind of attributes or values a column can hold in the database table. When we dont provide value for a. NOT NULL constraint makes sure that a column does not hold NULL value.
Constraints that are applied in the data model is called Implicit constraints. Unique constraints Unique constraints ensure that the values in a set of columns are unique and not null for all rows in. Types of constraints NOT NULL constraints NOT NULL constraints prevent null values from being entered into a column.
Constraints could be either at the column level or at the table level. CHECK Constraint The CHECK constraint ensures that all the values in a column satisfies certain conditions. Various types of integrity constraints are-.
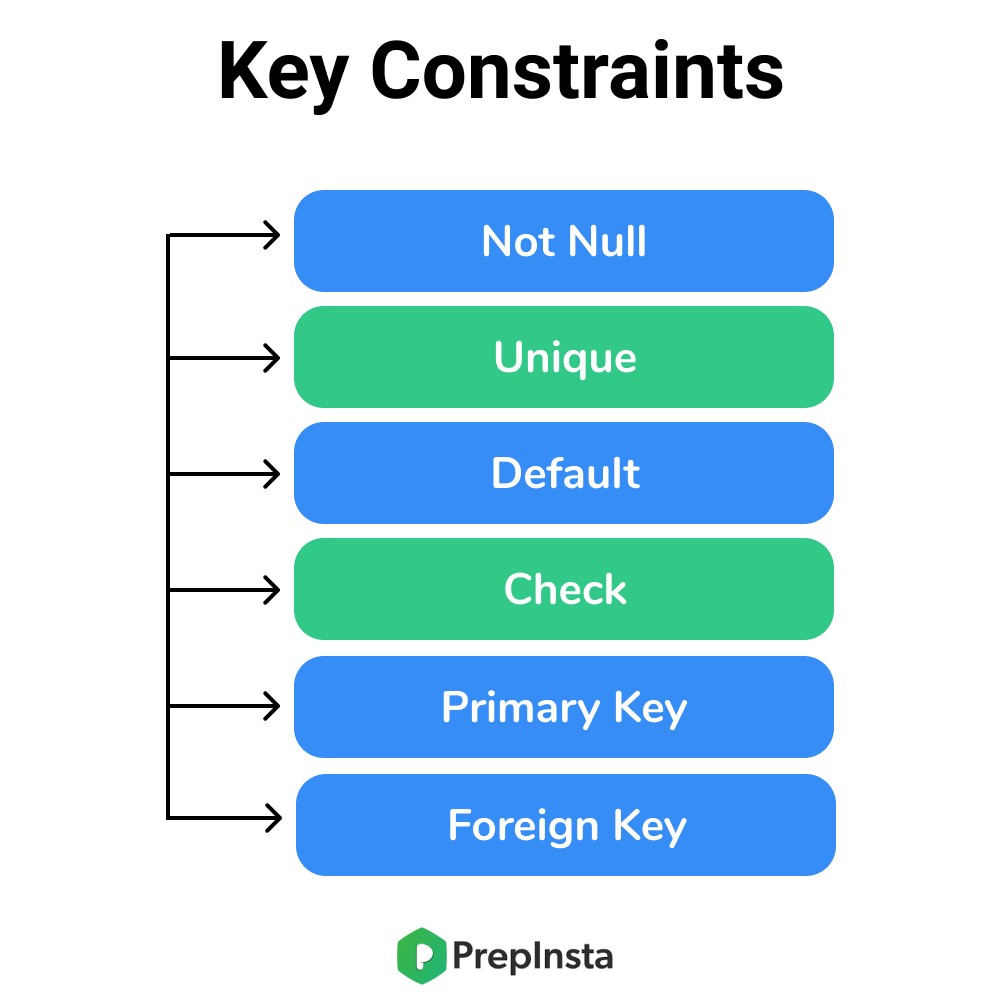
Types of SQL Constraints. This constraint specifies the number of instances of an entity that are. There are a number of key constraints in SQL that ensure that an entity or record is uniquely or differently identified in the database.
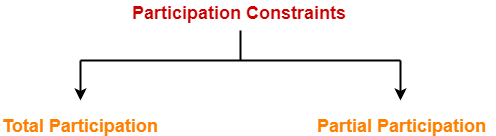
In a Relationship Participation constraint specifies the presence of an entity when it is related to another entity in a relationship type. Constraints are used for modeling limitations on the relations between entities. Referential integrity constraint state happens where relation refers to a key attribute of a different or same relation.
How to find cardinality. If a column has a unique. If there is any violation between the constraint and the data action the action is aborted.
Unique and primary keys are the supported unique constraints. There are two types of constraints that come under domain constraint and they are. FOREIGN Key Uniquely identifies a rowrecord in any of the given database table.
Provides a uniquedistinct values to specified columns. Constraints can be categorized into five types. There are two types of constraints on the Entity Relationship ER model.
Null values are the values that are unassigned or we can also say that which are unknown or the missing attribute values and by default a column can hold the null values. Provides a default value to a column if none is specified. Mapping cardinality or cardinality ratio.
This constraint is used when you do not want any value in that particular column to be a Null value. This type of constraint allows us to define a value to be used for a given column when no data is provided at. A unique constraint also referred to as a unique key constraint is a rule that forbids duplicate values in one or more columns within a table.
A foreign key is an important attribute of a relation which should be referred to in other relationships. Some of the key constraints in SQL are. This means that we cannot insert a Null value for that column while inserting a.
Column level constraints are applied only to one column whereas table level constraints are applied to the entire table. It is most useful in describing the relationship sets that involve more than two entity sets. SQL constraints are used to specify rules for the data in a table.
The UNIQUE and PRIMARY KEY constraints both provide a guarantee for uniqueness for a column or set of columns. Different Kinds of SQL Constraints. CHECK checks for the predefined conditions before inserting the data inside the table.
These constraints specify the number of entity instances which associates with instances of another entity. Constraints are used to limit the type of data that can go into a table. You define data type length or size is null value allowed is the value unique or not for an.
Constraints can be divided into the following two types Column level constraints. These are called as schema-based constraints or Explicit constraints. PRIMARY Key Uniquely identifies each rowrecord in a database table.
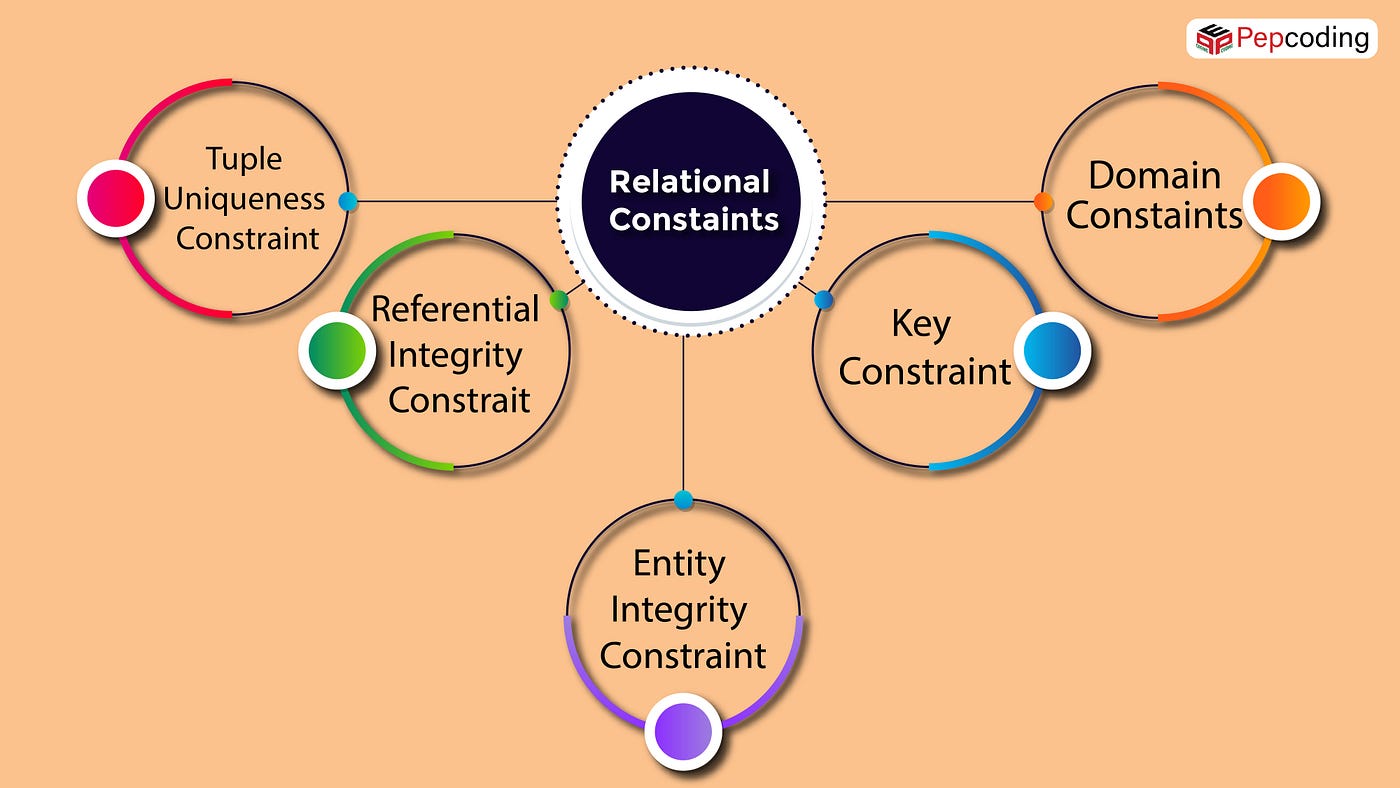
Types of constraints NOT NULL. Constraints that are directly applied in the schemas of the data model by specifying them in the DDLData Definition Language. Constraints in the databases can be categorized into 3 main categories.
DBMS Database Big Data Analytics. A mapping constraint is a data constraint that expresses the number of entities to which another entity can be related via a relationship set. Below given are different kinds.
By default a column can hold NULL values. This ensures the accuracy and reliability of the data in the table. UNIQUE Constraint Ensures that all values in a column are different.
CHECK constraints allow us to define a logical condition that will generate an error if it returns FALSE. There are four types of integrity constraints in DBMS.
Participation Constraints Dbms Gate Vidyalay

Domain Constraints In Dbms Database Management System
Relational Database Constraints Types Of Database Constraints By Pepcoding Medium

Relational Model Constraints Youtube
Key Constraints In Dbms Prepinsta
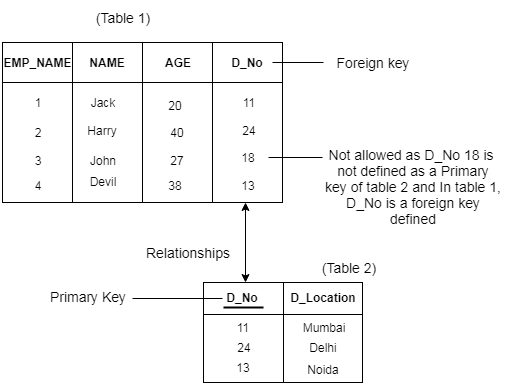
Dbms Integrity Constraints Javatpoint
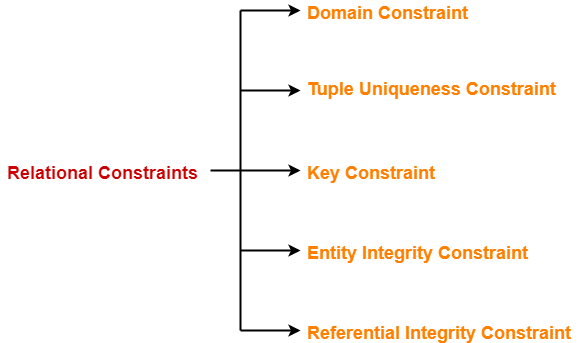
Constraints In Dbms Types Of Constraints In Dbms Gate Vidyalay
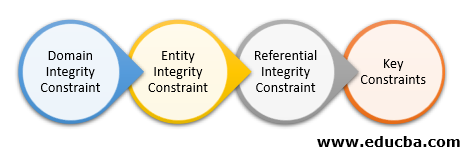
Integrity Constraints In Dbms Types Of Integrity Constraints In Dbms

Explain The Various Types Of Constraints On Relationship Types Of The E R Model
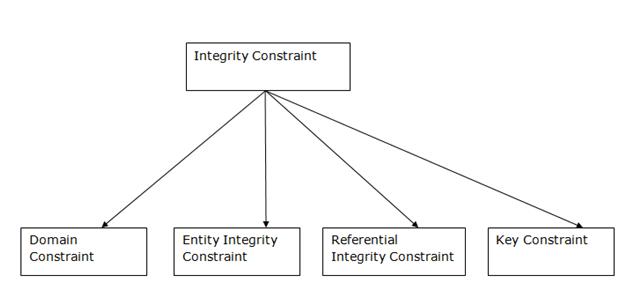
Dbms Integrity Constraints Javatpoint
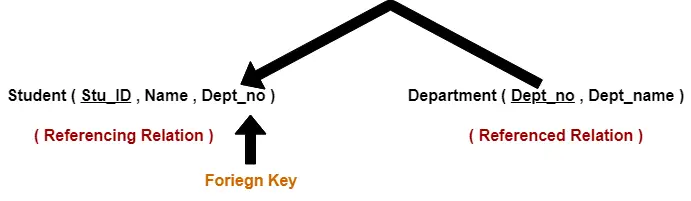
Constraints In Dbms Types Of Constraints In Dbms Gate Vidyalay

Constraints On Generalization Geeksforgeeks
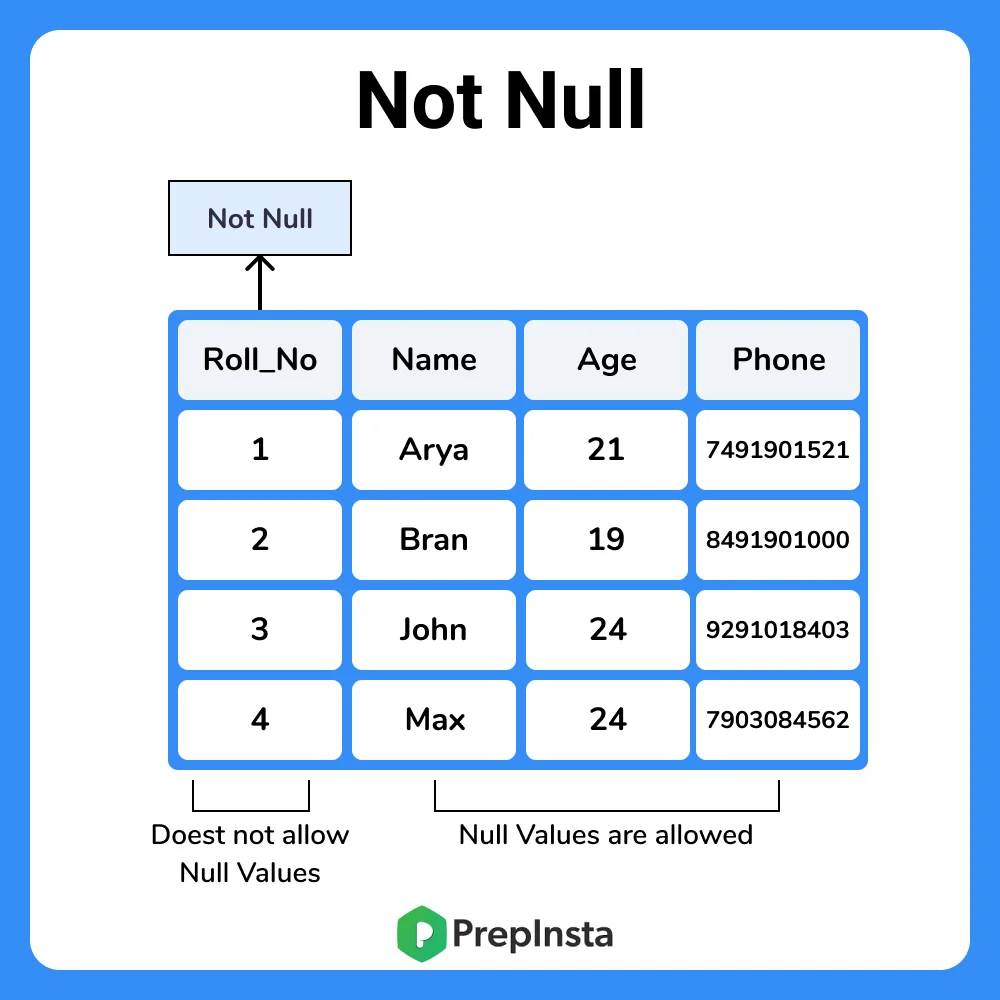
Key Constraints In Dbms Prepinsta

Integrity Constraints In Dbms Scaler Topics

Integrity Constraints In Dbms Types Of Integrity Constraints In Dbms
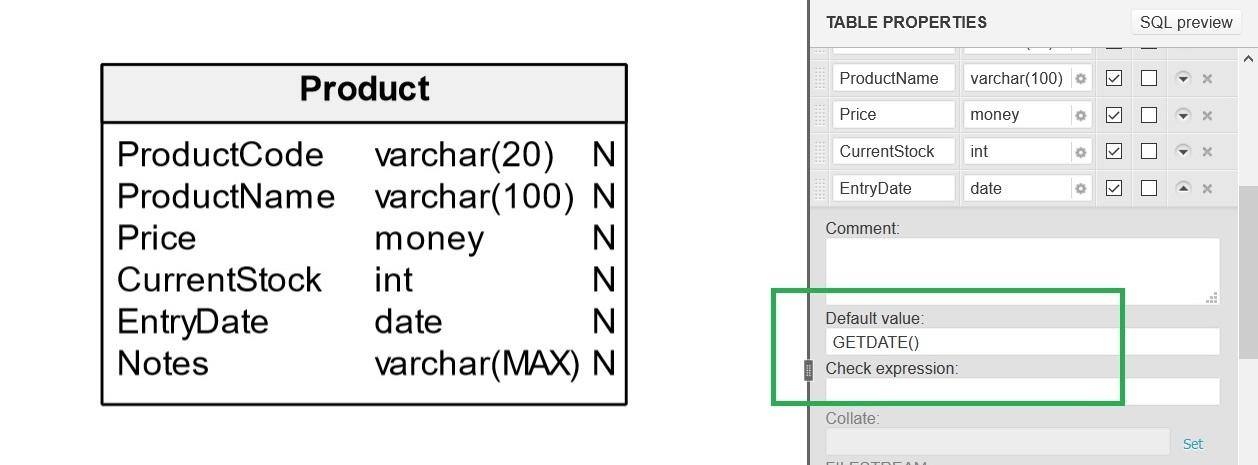
What Are The Different Types Of Database Constraints Vertabelo Database Modeler
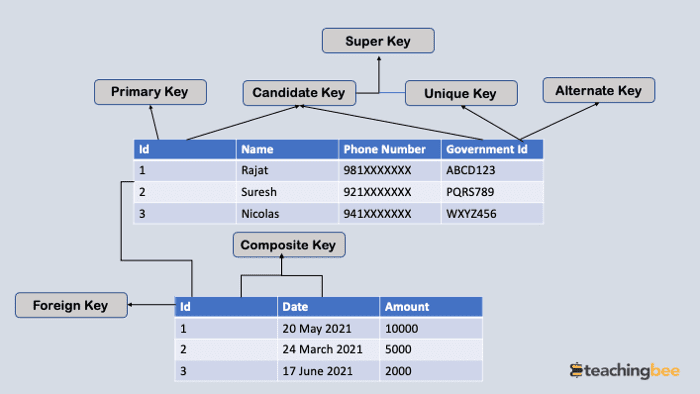
Key Constraints In Dbms Every Dba Should Know
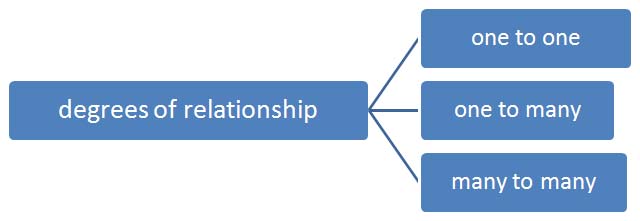
What Is Cardinality Types With Example In Dbms
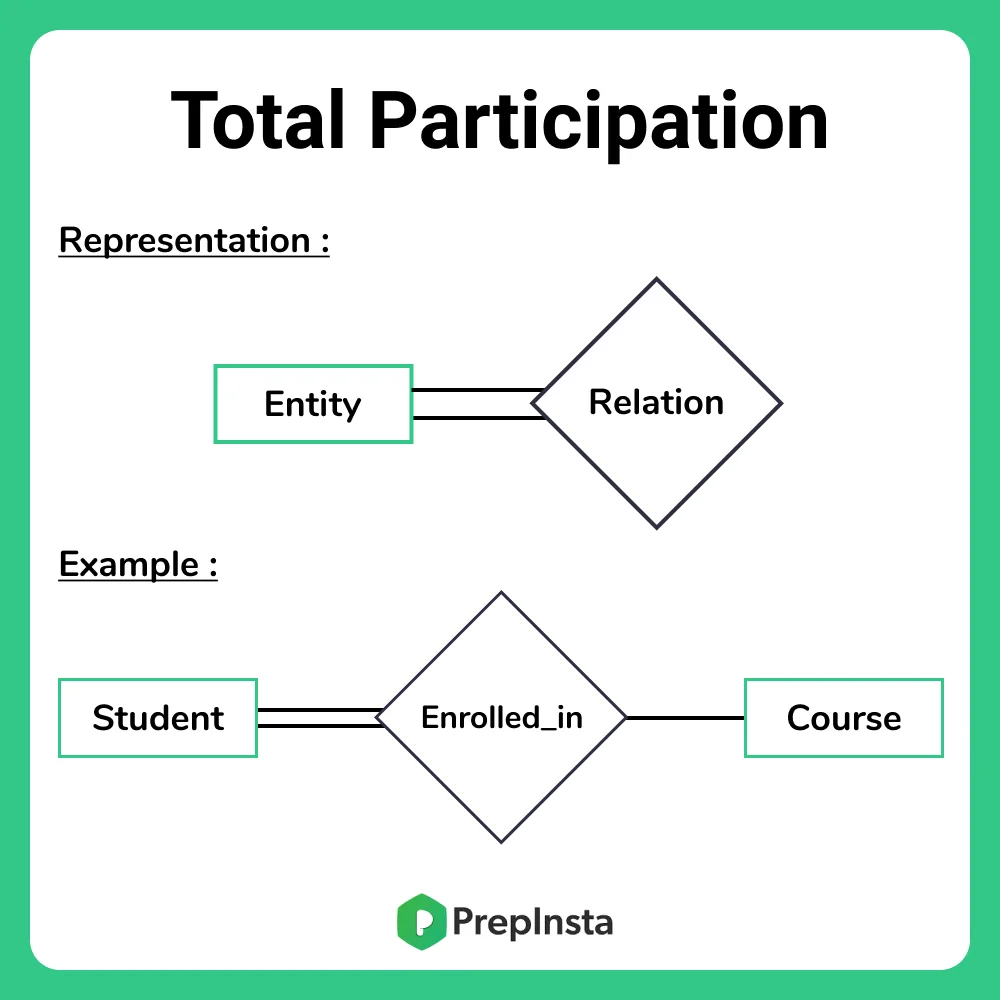
Participation Constraints In Dbms Database Management System
Comments
Post a Comment